Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Microsoft Fabric is a data analytics SaaS product that combines Microsoft’s analytics tools into one experience. Fabric Data Factory offers workflow orchestration, data movement, replication, and transformation at scale, similar to Azure Data Factory (ADF). If you’re looking to modernize your ADF investments, this guide will help you understand migration considerations, strategies, and approaches.
Migrating from ADF and Synapse pipelines to Fabric Data Factory offers several benefits:
- Integrated pipeline features like email and Teams activities for message routing during pipeline execution.
- Built-in CI/CD features (deployment pipelines) without needing external Git integration.
- Workspace integration with OneLake for streamlined analytics management.
- Easy semantic data model refreshes with integrated pipeline activities.
Fabric is designed for both self-service and IT-managed enterprise data. It scales to meet the needs of large organizations, offering secure, manageable, and accessible solutions.
With the growth of data volumes and complexity, Fabric empowers data integration developers and solutions with advanced features. Many customers are exploring whether to consolidate their data integration solutions within Fabric. Common questions include:
- Does Fabric support all the functionality we rely on?
- What unique capabilities does Fabric offer?
- How do we migrate existing pipelines to Fabric?
- What’s Microsoft’s roadmap for enterprise data ingestion?
Platform differences
Migrating an entire ADF instance involves understanding key differences between ADF and Fabric Data Factory. This section highlights those differences.
For a detailed comparison of features, see Compare Data Factory in Fabric and Azure Data Factory.
This section covers the following key differences:
- Integration runtimes: Fabric uses cloud-based compute by default, while ADF requires configuring integration runtimes. Fabric also supports the on-premises Data Gateway for local data access and the Virtual Network Data Gateway for secure network connectivity.
- Pipelines: Fabric pipelines include additional SaaS-based activities and differ in JSON definitions.
- Linked services: Fabric replaces Linked Services with Connections defined within activities.
- Datasets: Fabric eliminates datasets, defining data properties inline within activities.
- Dataflows: Fabric dataflows use Power Query, while ADF data flows rely on a different execution engine and language.
- Triggers: Fabric integrates triggers into its Activator framework, unlike ADF’s standalone triggers.
- Debugging: Fabric simplifies debugging by removing the need for a separate debug mode.
- Change Data Capture: Fabric manages incremental data movement through Copy jobs instead of CDC artifacts.
- Azure Synapse Link: Fabric replaces Synapse Link with mirroring features for data replication.
- SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS): Fabric doesn’t currently support SSIS IRs but allows invoking ADF pipelines for SSIS execution.
- Invoke pipeline activity: Fabric enhances ADF’s Execute pipeline activity with cross-platform invocation.
Integration runtimes
In ADF, integration runtimes (IRs) are configuration objects that define compute resources for data processing. These include cloud compute, self-hosted IRs (SHIRs) for on-premises connectivity, SSIS IRs for SQL Server Integration Services, and VNet-enabled cloud IRs.

Fabric, as a SaaS product, simplifies this by using cloud-based compute in the region of your Fabric capacities. SSIS IRs aren’t available in Fabric. For on-premises connectivity, use the on-premises Data Gateway (OPDG). For secured network connectivity, use the Virtual Network Data Gateway.
When migrating, you don’t need to move public network Azure IRs. Recreate SHIRs as OPDGs and VNet-enabled Azure IRs as Virtual Network Data Gateways.

Pipelines
Pipelines in ADF handle workflows for data movement, transformation, and orchestration. Fabric pipelines are similar but include additional components like native activities for emails, Teams, and semantic model refreshes.
The JSON definitions for Fabric pipelines differ slightly from ADF, so you can’t directly copy/paste or import/export pipeline JSON. Rebuild ADF pipelines in Fabric using the same workflow models and skills, but note that Linked Services and Datasets from ADF don’t exist in Fabric.
Linked services
In ADF, Linked Services define connectivity properties for data stores. In Fabric, recreate these as Connections within activities like Copy and Dataflows.
Datasets
Datasets in ADF define data properties like type, columns, and location. In Fabric, these properties are defined inline within pipeline activities and Connection objects.
Dataflows
Fabric Data Factory uses dataflows for code-free data transformation, built on Power Query. In ADF, similar functionality is called data flows, which use a different interface and execution engine. Recreate ADF data flows as Fabric dataflows when migrating.
Triggers
Triggers in ADF execute pipelines based on schedules, events, or custom triggers. Fabric uses a similar concept but integrates triggers into its Real-time Intelligence framework, called Activator.
Fabric schedules are platform-level entities, not specific to pipelines. Rebuild ADF schedule triggers as Fabric schedules and use Activator for other trigger types.

Debugging
Fabric simplifies debugging by eliminating ADF’s debug mode. You’re always in interactive mode. To test pipelines, select the play button in the editor. Use activity states to activate or deactivate specific activities for testing.
Change Data Capture
ADF’s Change Data Capture (CDC) feature enables incremental data movement. In Fabric, recreate CDC artifacts as Copy job items for similar functionality. See Copy job for details.
Azure Synapse Link
Synapse Link, used in Synapse pipelines, replicates data from SQL databases to data lakes. In Fabric, recreate these as Mirroring items. See mirroring in Fabric.
SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS)
Fabric doesn’t support SSIS IRs. Currently, to execute SSIS packages, use an ADF pipeline and call it from Fabric using the Invoke pipeline activity. See Invoke pipeline activity.
Invoke pipeline activity
Fabric’s Invoke pipeline activity enhances ADF’s Execute pipeline activity. Use it to call ADF pipelines inline from Fabric pipelines, maintaining ADF-specific features like Mapping Data Flows or SSIS.
Sample migration scenarios
Migrating from ADF to Fabric can involve different strategies depending on your use case. This section outlines common migration paths and considerations to help you plan effectively.
- Scenario 1: ADF pipelines and data flows
- Scenario 2: ADF with CDC, SSIS, and Airflow
- Scenario 3: Git-enabled Data Factory migration
Scenario 1: ADF pipelines and data flows
Modernize your ETL environment by migrating pipelines and data flows to Fabric. Plan for these elements:
- Recreate Linked Services as Connections.
- Define dataset properties inline in pipeline activities.
- Replace SHIRs (self-hosted integration runtimes) with OPDGs (on-premises data gateways) and VNet IRs with Virtual Network Data Gateways.
- Rebuild unsupported ADF activities using Fabric alternatives or the Invoke pipeline activity. Unsupported activities include:
- Data Lake Analytics (U-SQL), a deprecated Azure service.
- Validation activity, which can be rebuilt using Get Metadata, pipeline loops, and If activities.
- Power Query, which is fully integrated into Fabric as dataflows where M code can be reused.
- Notebook, Jar, and Python activities can be replaced with the Databricks activity in Fabric.
- Hive, Pig, MapReduce, Spark, and Streaming activities can be replaced with the HDInsight activity in Fabric.
As an example, here's ADF dataset configuration page, with its file path and compression settings:
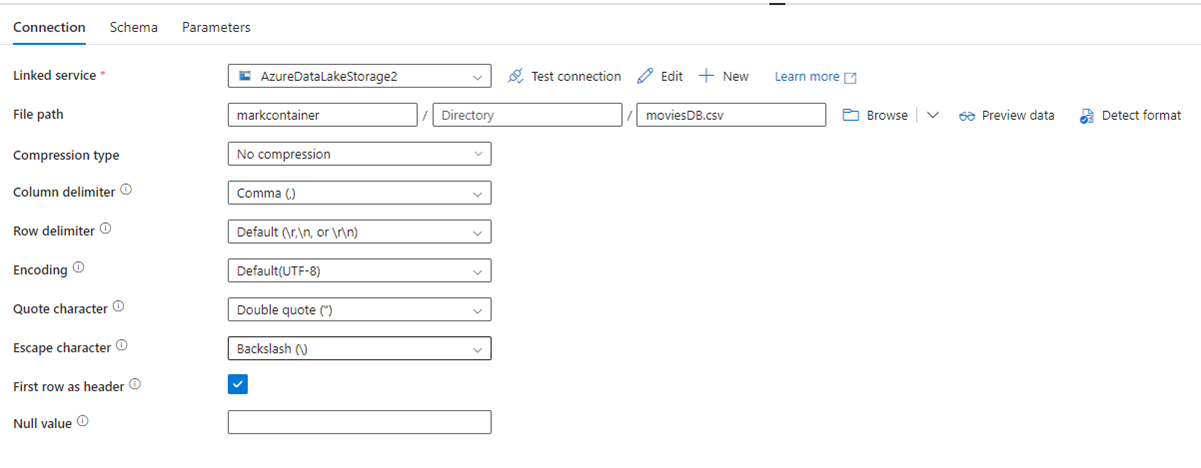
And here's a Copy activity for Data Factory in Fabric, where compression and file path are inline in the activity:

Scenario 2: ADF with CDC, SSIS, and Airflow
Recreate CDC as Copy job items. For Airflow, copy your DAGs into Fabric’s Apache Airflow offering. Execute SSIS packages using ADF pipelines and call them from Fabric.
Scenario 3: Git-enabled Data Factory migration
If your ADF or Synapse factories are connected to an external Git provider like Azure DevOps (ADO) or GitHub, you’ll need to migrate these items to a Fabric workspace. This involves setting up Git integration in Fabric and aligning your workflows with Fabric’s CI/CD capabilities. See Git integration in Fabric.
Fabric offers two primary CI/CD options:
- Git integration: Link your Fabric workspace to an external Git repository, such as ADO or GitHub, for version control and code management.
- Built-in deployment pipelines: Use Fabric’s native pipelines to promote code across environments without needing an external Git repository.
Existing Git repositories from ADF or Synapse won’t work directly with Fabric. Create a new repository or use Fabric’s deployment pipelines.
Mount ADF instances in a Fabric workspace
You can mount an entire ADF factory in a Fabric workspace as a native item. This lets you manage ADF factories alongside Fabric artifacts within the same interface. The ADF UI remains fully accessible, allowing you to monitor, manage, and edit your ADF factory items directly from the Fabric workspace. However, execution of pipelines, activities, and integration runtimes still occurs within your Azure resources.
This feature is particularly useful for organizations transitioning to Fabric, as it provides a unified view of both ADF and Fabric resources, simplifying management and planning for migration.