Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Azure AI services help developers and organizations build responsible applications with ready to use and customizable APIs and models. In this article, you use Azure AI services to perform tasks that include: text analytics, translation, document intelligence, vision, image search, speech to text and text to speech, anomaly detection, and data extraction from web APIs.
Azure AI services help developers create applications that see, hear, speak, understand, and begin to reason. The Azure AI services catalog includes five pillars: Vision, Speech, Language, Web search, and Decision.
Prerequisites
Get a Microsoft Fabric subscription. Or, sign up for a free Microsoft Fabric trial.
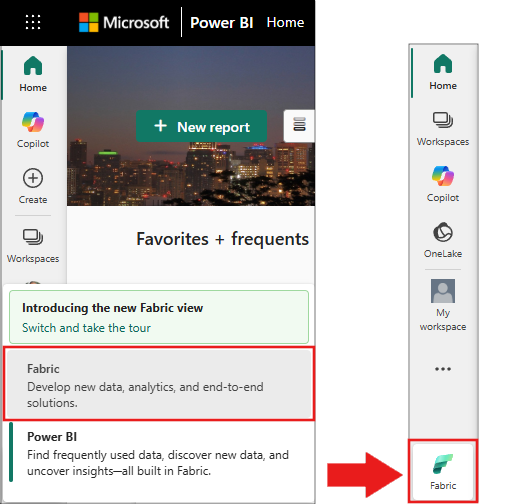
Sign in to Microsoft Fabric.
Use the experience switcher on the bottom left side of your home page to switch to Fabric.
- Create a notebook.
- Attach your notebook to a lakehouse. In the notebook, select Add to add an existing lakehouse or create a new one.
- Get an Azure AI services key. Follow Quickstart: Create a multi-service resource for Azure AI services. Copy the key value to use in the code samples below.
Prepare your system
Start by importing the required libraries, and initialize a Spark session.
from pyspark.sql.functions import udf, col, lit
from synapse.ml.io.http import HTTPTransformer, http_udf
from requests import Request
from pyspark.ml import PipelineModel
import os
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
# Start a Spark session.
spark = SparkSession.builder.getOrCreate()
Import the Azure AI services libraries. In the following code, replace the placeholder text <YOUR-KEY-VALUE> with your own keys, and set the location values for each service.
from synapse.ml.cognitive import *
# A general Azure AI services key for Text Analytics, Vision, and Document Intelligence (or use separate keys for each service).
service_key = "<YOUR-KEY-VALUE>" # Replace `<YOUR-KEY-VALUE>` with your Azure AI services key. See prerequisites for details.
service_loc = "eastus"
# A Bing Search v7 subscription key.
bing_search_key = "<YOUR-KEY-VALUE>" # Replace `<YOUR-KEY-VALUE>` with your Bing Search v7 subscription key. See prerequisites for details.
# An Anomaly Detector subscription key.
anomaly_key = "<YOUR-KEY-VALUE>" # Replace `<YOUR-KEY-VALUE>` with your Anomaly Detector key. See prerequisites for details.
anomaly_loc = "westus2"
# A Translator subscription key.
translator_key = "<YOUR-KEY-VALUE>" # Replace `<YOUR-KEY-VALUE>` with your Translator key. See prerequisites for details.
translator_loc = "eastus"
# An Azure Search key.
search_key = "<YOUR-KEY-VALUE>" # Replace `<YOUR-KEY-VALUE>` with your Azure Search key. See prerequisites for details.
Analyze sentiment in text
The Text Analytics service provides several algorithms for extracting intelligent insights from text. For example, use the service to analyze sentiment in input text. The service returns a score between 0.0 and 1.0: low scores indicate negative sentiment, and high scores indicate positive sentiment.
This code sample returns sentiment for three sentences.
# Create a DataFrame that's tied to its column names
df = spark.createDataFrame(
[
("I am so happy today, it's sunny!", "en-US"),
("I am frustrated by this rush hour traffic", "en-US"),
("The cognitive services on Spark aren't bad", "en-US"),
],
["text", "language"],
)
# Run the Text Analytics service with options
sentiment = (
TextSentiment()
.setTextCol("text")
.setLocation(service_loc)
.setSubscriptionKey(service_key)
.setOutputCol("sentiment")
.setErrorCol("error")
.setLanguageCol("language")
)
# Show the results in a table.
display(
sentiment.transform(df).select(
"text", col("sentiment.document.sentiment").alias("sentiment")
)
)
Perform text analytics for health data
Text Analytics for health extracts and labels medical information from unstructured text like doctor's notes, discharge summaries, clinical documents, and electronic health records.
This code sample analyzes text from doctor's notes and returns structured data.
df = spark.createDataFrame(
[
("20mg of ibuprofen twice a day",),
("1tsp of Tylenol every 4 hours",),
("6 drops of vitamin B-12 every evening",),
],
["text"],
)
healthcare = (
AnalyzeHealthText()
.setSubscriptionKey(service_key)
.setLocation(service_loc)
.setLanguage("en")
.setOutputCol("response")
)
display(healthcare.transform(df))
Translate text to another language
Translator is a cloud-based machine translation service that's part of the Azure AI services family of cognitive APIs for building intelligent apps. Translator integrates easily into your apps, websites, tools, and solutions. It lets you add multilingual experiences in 90 languages and dialects, and it works on any operating system for text translation.
The following code sample translates the input sentences into the target languages.
from pyspark.sql.functions import col, flatten
# Create a DataFrame with the sentences to translate
df = spark.createDataFrame(
[(["Hello, what is your name?", "Bye"],)],
[
"text",
],
)
# Run the Translator service.
translate = (
Translate()
.setSubscriptionKey(translator_key)
.setLocation(translator_loc)
.setTextCol("text")
.setToLanguage(["zh-Hans"])
.setOutputCol("translation")
)
# Show the translation results.
display(
translate.transform(df)
.withColumn("translation", flatten(col("translation.translations")))
.withColumn("translation", col("translation.text"))
.select("translation")
)
Extract information from a document into structured data
Azure AI Document Intelligence is part of Azure AI services and lets you build automated data processing software with machine learning. Use Azure AI Document Intelligence to identify and extract text, key-value pairs, selection marks, tables, and structure from your documents. The service outputs structured data that includes relationships from the original file, bounding boxes, confidence scores, and more.
The following code analyzes a business card image and extracts its information as structured data.
from pyspark.sql.functions import col, explode
# Create a DataFrame with the source files
imageDf = spark.createDataFrame(
[
(
"https://mmlspark.blob.core.windows.net/datasets/FormRecognizer/business_card.jpg",
)
],
[
"source",
],
)
# Run Azure AI Document Intelligence
analyzeBusinessCards = (
AnalyzeBusinessCards()
.setSubscriptionKey(service_key)
.setLocation(service_loc)
.setImageUrlCol("source")
.setOutputCol("businessCards")
)
# Show recognition results.
display(
analyzeBusinessCards.transform(imageDf)
.withColumn(
"documents", explode(col("businessCards.analyzeResult.documentResults.fields"))
)
.select("source", "documents")
)
Analyze and tag images
Azure AI Vision analyzes images to identify faces, objects, and natural language descriptions.
This code sample analyzes images and labels them with tags. Tags are one-word descriptions of objects, people, scenery, and actions in an image.
# Create a DataFrame with image URLs.
base_url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/cognitive-services-sample-data-files/master/ComputerVision/Images/"
df = spark.createDataFrame(
[
(base_url + "objects.jpg",),
(base_url + "dog.jpg",),
(base_url + "house.jpg",),
],
[
"image",
],
)
# Run Azure AI Vision to analyze images and extract information.
analysis = (
AnalyzeImage()
.setLocation(service_loc)
.setSubscriptionKey(service_key)
.setVisualFeatures(
["Categories", "Color", "Description", "Faces", "Objects", "Tags"]
)
.setOutputCol("analysis_results")
.setImageUrlCol("image")
.setErrorCol("error")
)
# Show the description tags.
display(analysis.transform(df).select("image", "analysis_results.description.tags"))
Search for images that are related to a natural language query
Bing Image Search searches the web to retrieve images related to a user's natural language query.
This sample uses a text query to find images of quotes. It outputs a list of image URLs related to the query.
# Number of images Bing returns per query
imgsPerBatch = 10
# List of offsets to page through the search results
offsets = [(i * imgsPerBatch,) for i in range(100)]
# Create a DataFrame of offsets to page through results
bingParameters = spark.createDataFrame(offsets, ["offset"])
# Run Bing Image Search with the text query
bingSearch = (
BingImageSearch()
.setSubscriptionKey(bing_search_key)
.setOffsetCol("offset")
.setQuery("Martin Luther King Jr. quotes")
.setCount(imgsPerBatch)
.setOutputCol("images")
)
# Create a transformer that extracts and flattens the Bing Image Search output into a single URL column
getUrls = BingImageSearch.getUrlTransformer("images", "url")
# Display the full results. Uncomment to use
# display(bingSearch.transform(bingParameters))
# Put both services into a pipeline
pipeline = PipelineModel(stages=[bingSearch, getUrls])
# Show the image URLs returned by the search
display(pipeline.transform(bingParameters))
Convert speech to text
The Azure AI Speech service converts spoken audio streams or files to text. The following code sample transcribes one audio file.
# Create a DataFrame with the audio URL in the 'url' column
df = spark.createDataFrame(
[("https://mmlspark.blob.core.windows.net/datasets/Speech/audio2.wav",)], ["url"]
)
# Run Azure AI Speech to transcribe the audio
speech_to_text = (
SpeechToTextSDK()
.setSubscriptionKey(service_key)
.setLocation(service_loc)
.setOutputCol("text")
.setAudioDataCol("url")
.setLanguage("en-US")
.setProfanity("Masked")
)
# Show the transcription results
display(speech_to_text.transform(df).select("url", "text.DisplayText"))
Transform text to speech
Text to speech is a service that lets you build apps and services that speak naturally. Choose from more than 270 neural voices across 119 languages and variants.
The following code sample converts text to an audio file.
from synapse.ml.cognitive import TextToSpeech
fs = ""
if running_on_databricks():
fs = "dbfs:"
elif running_on_synapse_internal():
fs = "Files"
# Create a dataframe with text and an output file location
df = spark.createDataFrame(
[
(
"Reading out loud is fun! Check out aka.ms/spark for more information",
fs + "/output.mp3",
)
],
["text", "output_file"],
)
tts = (
TextToSpeech()
.setSubscriptionKey(service_key)
.setTextCol("text")
.setLocation(service_loc)
.setVoiceName("en-US-JennyNeural")
.setOutputFileCol("output_file")
)
# Check that there are no errors during audio creation
display(tts.transform(df))
Detect anomalies in time series data
Anomaly Detector detects irregularities in time series data. This example uses the Anomaly Detector service to find anomalies in an entire time series.
# Create a DataFrame with the point data that Anomaly Detector requires
df = spark.createDataFrame(
[
("1972-01-01T00:00:00Z", 826.0),
("1972-02-01T00:00:00Z", 799.0),
("1972-03-01T00:00:00Z", 890.0),
("1972-04-01T00:00:00Z", 900.0),
("1972-05-01T00:00:00Z", 766.0),
("1972-06-01T00:00:00Z", 805.0),
("1972-07-01T00:00:00Z", 821.0),
("1972-08-01T00:00:00Z", 20000.0),
("1972-09-01T00:00:00Z", 883.0),
("1972-10-01T00:00:00Z", 898.0),
("1972-11-01T00:00:00Z", 957.0),
("1972-12-01T00:00:00Z", 924.0),
("1973-01-01T00:00:00Z", 881.0),
("1973-02-01T00:00:00Z", 837.0),
("1973-03-01T00:00:00Z", 9000.0),
],
["timestamp", "value"],
).withColumn("group", lit("series1"))
# Run Anomaly Detector to detect anomalies
anomaly_detector = (
SimpleDetectAnomalies()
.setSubscriptionKey(anomaly_key)
.setLocation(anomaly_loc)
.setTimestampCol("timestamp")
.setValueCol("value")
.setOutputCol("anomalies")
.setGroupbyCol("group")
.setGranularity("monthly")
)
# Show results with anomalies marked as True
display(
anomaly_detector.transform(df).select("timestamp", "value", "anomalies.isAnomaly")
)
Get information from arbitrary web APIs
Use any web service in your big data pipeline with HTTP on Spark. The following code sample uses the World Bank API to get information about different countries and regions around the world.
# Use any request from the Python requests library.
def world_bank_request(country):
return Request(
"GET", "http://api.worldbank.org/v2/country/{}?format=json".format(country)
)
# Create a DataFrame that specifies the countries to get data for.
df = spark.createDataFrame([("br",), ("usa",)], ["country"]).withColumn(
"request", http_udf(world_bank_request)(col("country"))
)
# Improve big data performance by using concurrency.
client = (
HTTPTransformer().setConcurrency(3).setInputCol("request").setOutputCol("response")
)
# Get the body of the response.
def get_response_body(resp):
return resp.entity.content.decode()
# Show country details from the response.
display(
client.transform(df).select(
"country", udf(get_response_body)(col("response")).alias("response")
)
)