Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies to:
SQL Server
In this quickstart, you create a new database, create a full backup of it, and then restore it.
For more detailed information, see Create a full database backup and Restore a database backup using SSMS.
Prerequisites
Create a test database
Open SQL Server Management Studio and connect to your SQL Server instance.
Open a New Query window.
Create your test database by using the following Transact-SQL (T-SQL) code.
USE [master]; GO CREATE DATABASE [SQLTestDB]; GO USE [SQLTestDB]; GO CREATE TABLE SQLTest ( ID INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY, c1 VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL, dt1 DATETIME NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE() ); GO USE [SQLTestDB]; GO INSERT INTO SQLTest (ID, c1) VALUES (1, 'test1'); INSERT INTO SQLTest (ID, c1) VALUES (2, 'test2'); INSERT INTO SQLTest (ID, c1) VALUES (3, 'test3'); INSERT INTO SQLTest (ID, c1) VALUES (4, 'test4'); INSERT INTO SQLTest (ID, c1) VALUES (5, 'test5'); GO SELECT * FROM SQLTest; GORefresh the Databases node in Object Explorer to see your new database.
Create a backup
To create a backup of your database, follow these steps by using SQL Server Management Studio or Transact-SQL:
- Open SSMS and connect to your SQL Server instance.
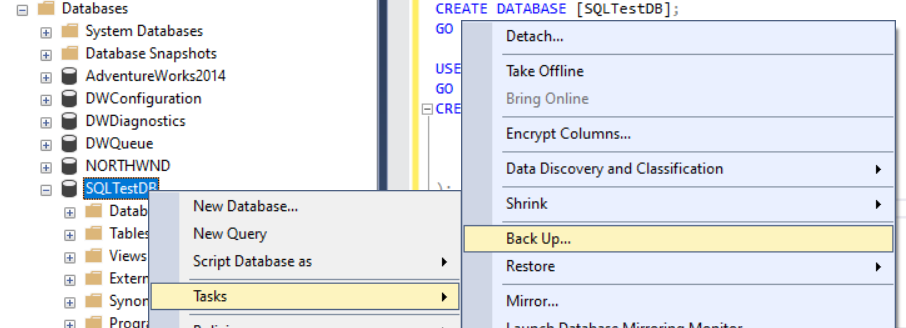
- Expand the Databases node in Object Explorer.
- Right-click the database, hover over Tasks, and then select Back up....
- Under Destination, confirm that the path for your backup is correct. If you need to change the path, select Remove to remove the existing path, and then select Add to type in a new path. You can use the ellipsis button (...) to navigate to a specific file.
- Select OK to create a backup of your database.
For more information about backup options, see BACKUP.
Restore a database
To restore your database, follow these steps:
Open SSMS and connect to your SQL Server instance.
Right-click the Databases node in Object Explorer and select Restore Database....

Select Device, and then select the ellipsis button (...) to locate your backup file.
Select Add and navigate to the location of your
.bakfile. Select the.bakfile, and then select OK.Select OK to close the Select backup devices dialog.
Select OK to restore your database.
Clean up resources
Run the following Transact-SQL command to remove the database you created, along with its backup history in the msdb database:
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_delete_database_backuphistory @database_name = N'SQLTestDB'
GO
USE [master];
GO
DROP DATABASE [SQLTestDB];
GO
Related content
- Restore SQL Server databases on Azure VMs
- Quickstart: Restore a database to Azure SQL Managed Instance with SSMS
- Restore a database from a backup in Azure SQL Database
- Back Up and Restore of SQL Server Databases
- SQL Server backup to URL for Azure Blob Storage
- Create a full database backup
- Restore a database backup using SSMS