Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
When scanning Snowflake data sources, Microsoft Purview supports extracting technical metadata, including:
- Server, databases, schemas, and tables, including the columns; views including the columns, foreign keys, and unique constraints.
- Stored procedures, including the parameter dataset and result set.
- Functions, including the parameter dataset.
- Pipes, stages, and streams, including the columns.
- Tasks and sequences.
Configure Data Map scan to catalog Snowflake data in Microsoft Purview
Register a Snowflake source
To register a new Snowflake source in Unified Catalog, follow these steps:
- Sign into the Microsoft Purview portal.
- Select the Data Map solution card. If the Data Map solution card isn't displayed, select View all solutions and then select Data Map from the Core section.
- Select Register.
- On Register sources, select Snowflake.
Set up a Data Map scan
- Select the registered Snowflake source.
- Select + New scan.
- Provide the below details:
- Name: The name of the scan
- Connect via integration runtime: Select the Azure autoresolved integration runtime, Managed Virtual Network IR, or SHIR according to your scenario.
- Host for connection: Choose the endpoint used to establish connection to Snowflake during scan. You can choose from the server URL, or the other hosts that you configured in data source.
- Credential: Select the credential to connect to your data source. Make sure to:
- Select Basic Authentication while creating a credential.
- Provide the user name used to connect to Snowflake in the User name input field.
- Store the user password used to connect to Snowflake in the secret key.
- Warehouse: Specify the name of the warehouse instance used to empower scan in capital case. The default role assigned to the user specified in the credential must have USAGE rights on this warehouse.
- Databases: Specify one or more database instance names to import in capital case. Separate the names in the list with a semi-colon (;). For example, DB1;DB2. The default role assigned to the user specified in the credential must have adequate rights on the database objects.
- Schema: List subset of schemas to import expressed as a semicolon separated list.
- Select Test connection to validate the settings (available when using Azure Integration Runtime).
- Select Continue.
- Select a scan rule set for classification. You can choose between the system default, existing custom rule sets, or create a new rule set inline.
- Review your scan and select Save and Run.
Once scanned, the data asset in Snowflake will be available on the Unified Catalog search. For more details about how to connect and manage Snowflake in Microsoft Purview, follow this document.
Important
When the object is deleted from the data source, the subsequent scan won't automatically remove the corresponding asset in Microsoft Purview.
Configure private endpoint to Snowflake private link
To configure private endpoint to Snowflake private link using managed virtual network, follow this step by step guidance.
Azure Private Link provides private connectivity to Snowflake by ensuring that access to Snowflake is through a private IP address. The network traffic flows to the Snowflake Virtual Network using the Microsoft backbone and avoids the public internet. This significantly simplifies the network configuration by keeping access rules private while providing secure and private communication.
- Execute
SYSTEM$WHITE_LIST and SYSTEM$WHITE_LIST_PRIVATELINKto obtain theSNOWFLAKE_DEPLOYMENT, SNOWFLAKE_DEPLOYMENT_REGIONLESS and OCSP_CACHEvalues for public andwhite_listhosts. Example script is provided in this document. - Execute
SYSTEM$GET_SNOWFLAKE_PLATFORM_INFO()asACCOUNTADMINto obtain the snowflake-vnet-subnet-ids values. The Subscription ID for the Private Link of the Snowflake’s Azure tenant is obtained from this. Example script is provided in this document. The subscription id is the one, which has the resource group azure-prod or if it is not present, then it would be the deployment-infra-rg or something similar. The Resource group and Subscription ID may change in the future. Contact Snowflake support to get the actual Subscription ID details. - Create a private endpoint for private link under the Managed private endpoints section in the Manage menu of the Data Factory Studio. For more information on Data Factory managed private endpoints refer to the Microsoft documentation.
- Select Private link service to configure the managed endpoint for the Snowflake private link.
- The resource ID for the target Snowflake private link is of the following format:
/subscriptions/(subscription_id)/resourcegroups/az(region)-privatelink/providers/microsoft.network/privatelinkservices/sf-pvlinksvc-az(region).
- To obtain region-id and Fully qualified name, run
SYSTEM_WHITE_LISTandSYSTEM_WHITE_LIST_PRIVATELINKto obtain theSNOWFLAKE_DEPLOYMENT,SNOWFLAKE_DEPLOYMENT_REGIONLESS, andOCSP_CACHEvalues for public and allowlist hosts. - To obtain Subscription ID, run
SYSTEM$GET_SNOWFLAKE_PLATFORM_INFO()asACCOUNTADMINto obtain the snowflake-vnet-subnet-ids values. The Subscription ID for the Private Link of the Snowflake’s Azure tenant is obtained from this.
- For the fully qualified name, add the
SNOWFLAKE_DEPLOYMENT, SNOWFLAKE_DEPLOYMENT_REGIONLESSandOCSP_CACHEof both the public and private link host from Step 1. - The Provisioning state should be Succeeded, and the Approval state should be pending. If the Provisioning state has failed, check the values provided and repeat the process with the correct values.
- Since the Private link is in Snowflake’s Azure Subscription, the support ticket needs to be raised to Snowflake to approve the private endpoint connection. Provide the managed private endpoint resource id and the managed approvals link in the Azure portal.
- Once the Snowflake support confirmed the connection is approved, the managed endpoint approval state should be approved and ready to be utilized.
- Execute
SYSTEM$GET_PRIVATELINK_AUTHORIZED_ENDPOINTS()to check the connection in Snowflake. You can also execute the following query with a warehouse to get it in a readable format. Example script is provided in this document. - The linked service is configured with the Snowflake connection, and it makes use of the private endpoint to connect to Snowflake via private link.
Set up connection to Snowflake data source for data quality scan
At this point, the scanned asset is ready for cataloging and governance. Associate the scanned asset to the data product in a Governance Domain Sele. At the Data Quality Tab, add a new Azure SQL Database Connection: Get the Database Name entered manually.
In the Microsoft Purview portal, open Unified Catalog.
Under Health management, select Data quality.
Select a governance domain from the list, then select Connections from the Manage dropdown list.
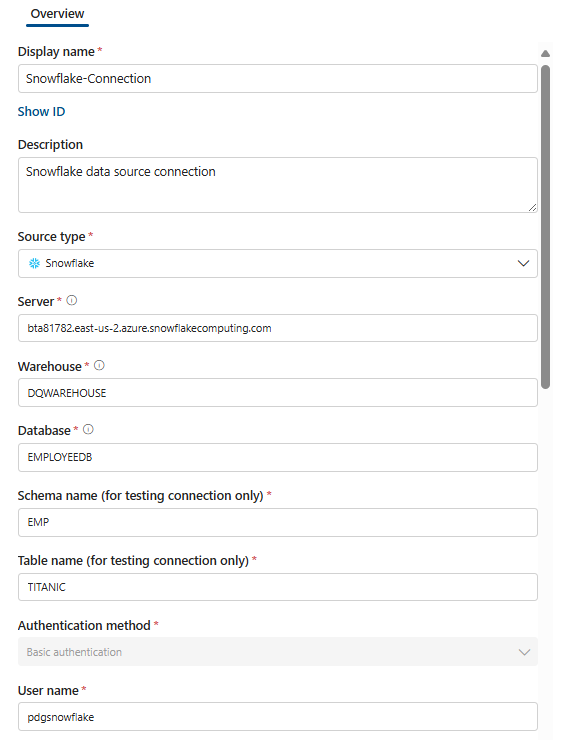
Configure connection on the Connections page:
- Add connection name and description.
- Select source type Snowflake.
- Add Server name, Warehouse name, Database name, Schema name, and Table name.
- Select authentication method - Basic authentication.
- Add User name.
- Add Credentials:
- Add Azure subscription
- Key vault connection
- Secret name
- Secret version
- Select the Enable managed V-Net checkbox if your Snowflake is running on Azure Virtual Network.
- Select the Azure Region.
- Add Private Link Resources ID.
- Add Fully Qualified Domain Name.
Test the connection to make sure it works. If you're using Virtual Network, then the test connection feature isn't supported.
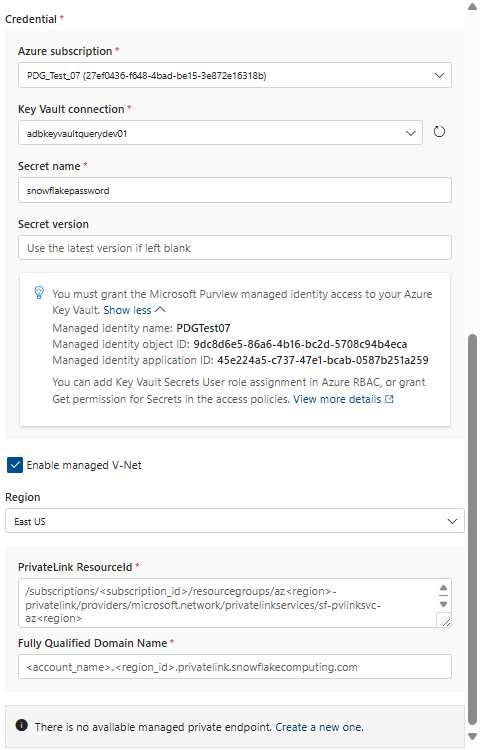
The resource ID for the target Snowflake private link is of the following format: /subscriptions/(subscription_id)/resourcegroups/az(region)-privatelink/providers/microsoft.network/privatelinkservices/sf-pvlinksvc-az(region).
- To obtain region-id and Fully qualified name, run
SYSTEM_WHITE_LISTandSYSTEM_WHITE_LIST_PRIVATELINKto obtain theSNOWFLAKE_DEPLOYMENT,SNOWFLAKE_DEPLOYMENT_REGIONLESS, andOCSP_CACHEvalues for public and allowlist hosts. - To obtain Subscription ID, run
SYSTEM$GET_SNOWFLAKE_PLATFORM_INFO()asACCOUNTADMINto obtain the snowflake-vnet-subnet-ids values. The Subscription ID for the Private Link of the Snowflake’s Azure tenant is obtained from this.
Important
- Data quality stewards need read only access to Snowflake to set up the data quality connection.
- The Snowflake connector doesn't accept https://. Remove https:// when you add the server name to configure data source connection.
- If public access is disabled, you need to select the Allow trusted Microsoft services checkbox for Key Vault. This is required only for Key Vault, not for your Snowflake workspace.
Profiling and data quality scanning for data in Snowflake
After completed connection setup successfully, you can profile, create and apply rules, and run a data quality scan of your data in Snowflake. Follow the step-by-step guideline described in below documents: